
- #GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD HOW TO#
- #GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD FULL#
- #GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD CODE#
- #GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD PASSWORD#
But this is not something that we recommend, as it will put all of your private project files on the open web for anyone with internet access to view and download. Technically, you could temporarily change the visibility settings of a private repository, making it public to clone. You can also clone repositories owned by someone else as a way to contribute to the project.
#GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD FULL#
This process pulls a full copy of the repo data from, which includes all of the file versions and folders of the project. When you clone a repository, it creates a local copy on your computer so you can sync it between two locations.Ĭloning a repository can make it easier to add files, remove files, fix merge issues, and push large commits. Whenever you create a repository, it exists remotely on GitHub. It’s also worth noting that users with certain administrative permissions have the ability to change the visibility of an existing repository from public to private or vice versa. Private repositories are only accessible by the owner, people who have been directly given access to the repo, and certain members of an organization. Public repositories in GitHub are accessible to anyone on the internet. You can determine these settings when you first create a new repo in GitHub. You can grant access to collaborators, giving them the ability to work on the project simultaneously.įor repositories owned by an organization, the members and collaborators can all be managed using GitHub’s permission levels and organizational repository roles.Īll GitHub repositories fall into one of two categories-public or private. If you own a repository, you can restrict access to your files and manage your project’s visibility. You have the ability to own repositories independently, or share ownership of them with other users in an organization.

GitHub repositories contain all project files and version histories of each file. This background information helps you make sense of the process behind the cloning steps-so you’re not just blindly following directions. Having a firm grasp of how GitHub repos work will make your life much easier when you’re cloning them. Step #1: Understand the Differences Between Public and Private Repositories in GitHub
#GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD HOW TO#
This step-by-step guide will show you how to clone a private GitHub repository and walk you through common stumbling blocks you might encounter along the way. But when it comes to private repositories, the process can be a bit tricker.
#GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD PASSWORD#
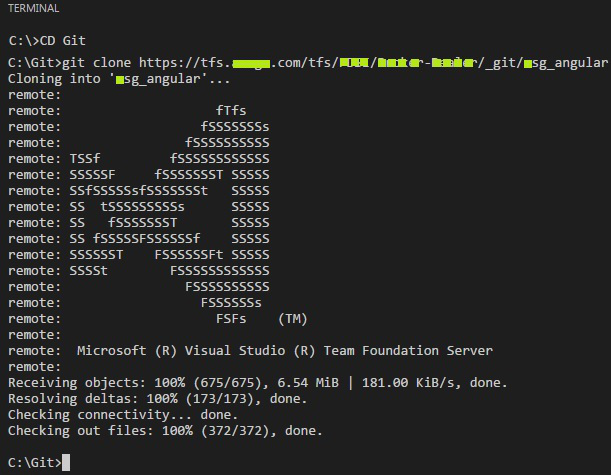
Keep in mind that using an SSH URL to clone a repository is a more secure and recommended option, as it allows you to authenticate using your SSH key instead of a password or PAT.Cloning a repository in GitHub is relatively straightforward.
You can then enter your GitHub username as usual, and your PAT as your password. This command will save your credentials to a local file, so you don’t have to enter them every time you interact with GitHub. Option 2: Use an SSH URLĪlternatively, you can configure Git to use your PAT for all future interactions with GitHub by running the following command in your terminal: git config -global credential.helper store When prompted for your GitHub credentials while cloning a repository using an HTTPS URL, paste your PAT as your password. For cloning repositories, you need to select the “repo” scope. Give your token a name and select the scopes you need. Next, you need to generate a new token by selecting the “Generate new token” button. Select “Developer settings,” and then “Personal access tokens.” Create a personal access token (PAT) on GitHub Here are the steps to follow: Option 1: Use a Personal Access Token (PAT) Step 1.
To fix the “Support for password authentication was removed” error in GitHub, you need to switch to using a personal access token (PAT) instead of a password for authentication. Remote: Please see for information on currently recommended modes of authentication.
#GIT CLONE COMMAND USERNAME PASSWORD CODE#
I was trying to push my latest committed code to the remote GitHub repository, but faced the following error message: remote: Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021. This means that if you try to clone a repository using an HTTPS URL and authenticate with a password, you will receive the following error message: “Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021.” Fortunately, you can fix this issue by switching to a personal access token (PAT) or an SSH URL. GitHub is a popular platform for version control and collaboration, but in August 2021, GitHub removed support for password authentication for HTTPS URLs. How to Fix “Support for password authentication was removed” error in GitHub

He has an excellent track record of blogging in areas like Docker, Kubernetes, IoT and AI. Avinash Bendigeri Follow Avinash is a developer-turned Technical writer skilled in core content creation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
